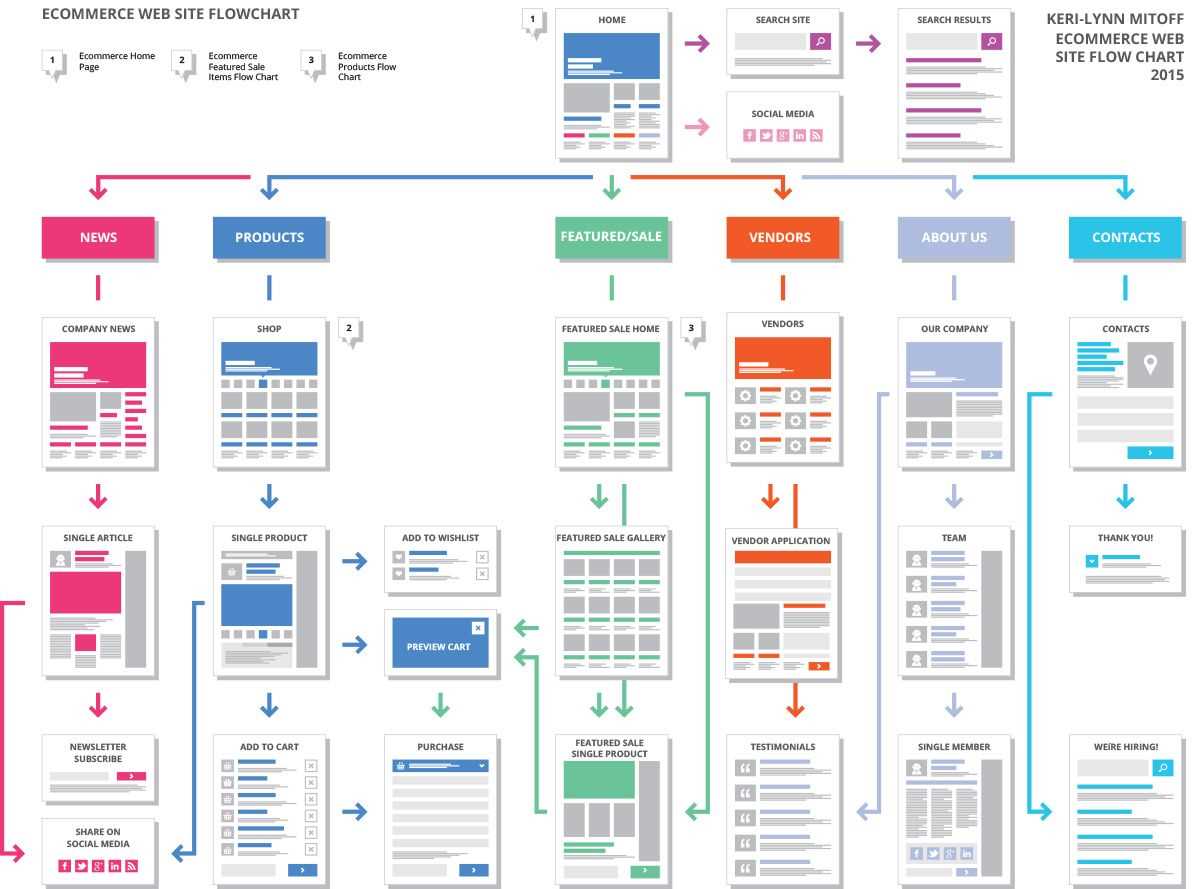
Designing a product or service requires a well-defined and organized process. One way to visualize and plan this process is by creating a design process flow diagram. This diagram outlines the steps and stages involved in the design process, helping teams and individuals understand and execute their tasks effectively.
Creating an effective design process flow diagram requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. It involves identifying key milestones, setting clear objectives, and establishing a timeline for each stage. This article will guide you through 10 essential steps to create an efficient and successful design process flow diagram.
Step 1: Define the project’s goals and objectives. Before creating a design process flow diagram, it’s crucial to clearly understand the project’s goals and objectives. This step ensures that the design process aligns with the desired outcomes and helps achieve the desired results.
Step 2: Identify the key stakeholders. Determine who will be involved in the design process and who the key decision-makers are. This step helps streamline communication and ensures that everyone’s input is considered throughout the design process.
Step 3: Map out the design process steps. Break down the design process into individual steps or stages. This step allows for a clear visual representation of the entire process and helps identify any gaps or redundancies in the workflow.
Step 4: Define the input and output for each step. Determine what inputs are required and what outputs are expected at each stage of the design process. This step ensures that designers and team members understand their responsibilities and deliverables.
Step 5: Establish a timeline and set deadlines. Create a timeline for each stage of the design process, including specific deadlines for key milestones. This step helps keep the project on track and ensures that everyone is aware of the time constraints.
Step 6: Assign tasks and responsibilities. Clearly define the tasks and responsibilities for each team member or department involved in the design process. This step promotes accountability and ensures that everyone knows what they need to do and when.
Step 7: Evaluate and refine the design process. Regularly review and evaluate the design process to identify areas for improvement. This step allows for continuous optimization and ensures that the design process remains effective and efficient.
Step 8: Share and communicate the design process with stakeholders. Once the design process has been created and refined, share it with the relevant stakeholders. This step promotes transparency and helps ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Step 9: Implement the design process. Put the design process into action and start working on the project. This step requires effective collaboration and communication among team members to execute the design process successfully.
Step 10: Monitor and measure the design process’s effectiveness. Continuously monitor and measure the design process’s effectiveness through key performance indicators (KPIs) and feedback from team members and stakeholders. This step allows for ongoing improvements and ensures that the design process aligns with the project’s goals.
Step 1: Determine the Objective of Your Flow Diagram
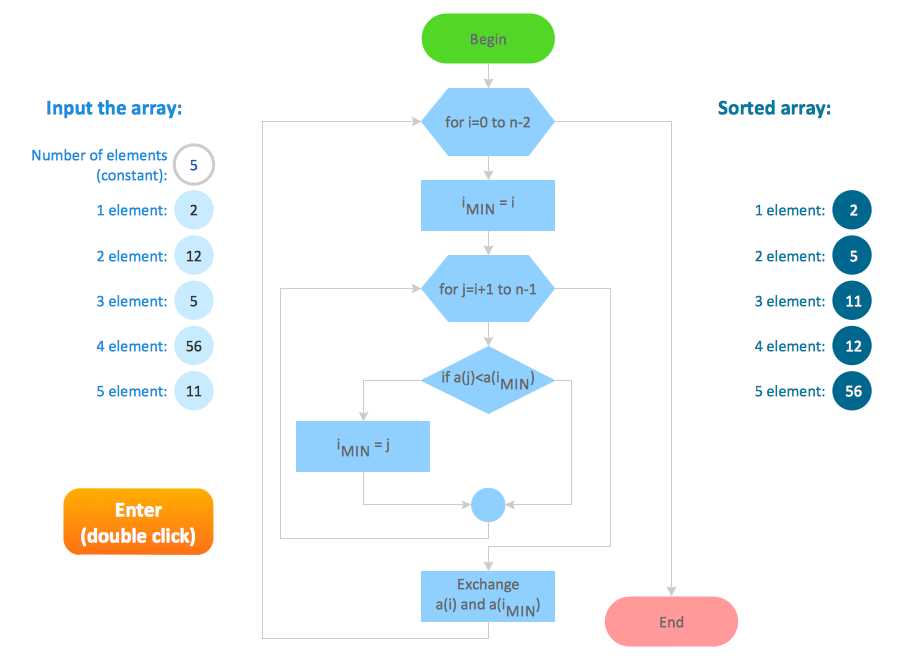
When creating an effective design process flow diagram, it is crucial to first clearly define the purpose and objective of the diagram. This step sets the foundation for the entire design process and ensures that all subsequent steps and decisions align with the intended goals.
To begin, consider what specific aspect of the design process you want to depict in the flow diagram. Are you focusing on the overall workflow from start to finish, or do you want to highlight a particular stage or sub-process? Clearly identifying the objective will help you determine the scope and level of detail needed for your diagram.
Additionally, it is important to understand the audience for your diagram. Are you creating it for team members, stakeholders, or clients? Knowing your audience will help you tailor the content and presentation style accordingly.
By defining the purpose of your flow diagram, you are setting a clear direction for the design process and ensuring that it effectively communicates the necessary information to the intended audience. This step helps establish a solid foundation for the subsequent steps in creating an effective design process flow diagram.
Step 2: Identify the Key Stakeholders
Identifying the key stakeholders is a crucial step in creating an effective design process flow diagram. Stakeholders refer to individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the design process or its outcomes. These can include clients, project managers, designers, developers, and end users, among others.
To identify the key stakeholders, it is important to consider the different roles and responsibilities that each stakeholder holds in the design process. This can be done by conducting interviews, surveys, or workshops with relevant individuals or groups. It is also important to consider the level of influence that each stakeholder has on the design process and its outcomes.
Once the key stakeholders have been identified, it is important to involve them in the design process and incorporate their inputs and feedback. This can help ensure that the design process is aligned with their goals and expectations and can increase the likelihood of a successful outcome. Communication and collaboration with the key stakeholders throughout the design process are essential for creating a design that meets their needs and requirements.
Overall, identifying the key stakeholders and involving them in the design process is an important step in creating an effective design process flow diagram. It helps ensure that the design process is informed by the perspectives and requirements of the relevant individuals or groups, increasing the chances of creating a successful design solution.
Step 3: Gather Information and Data
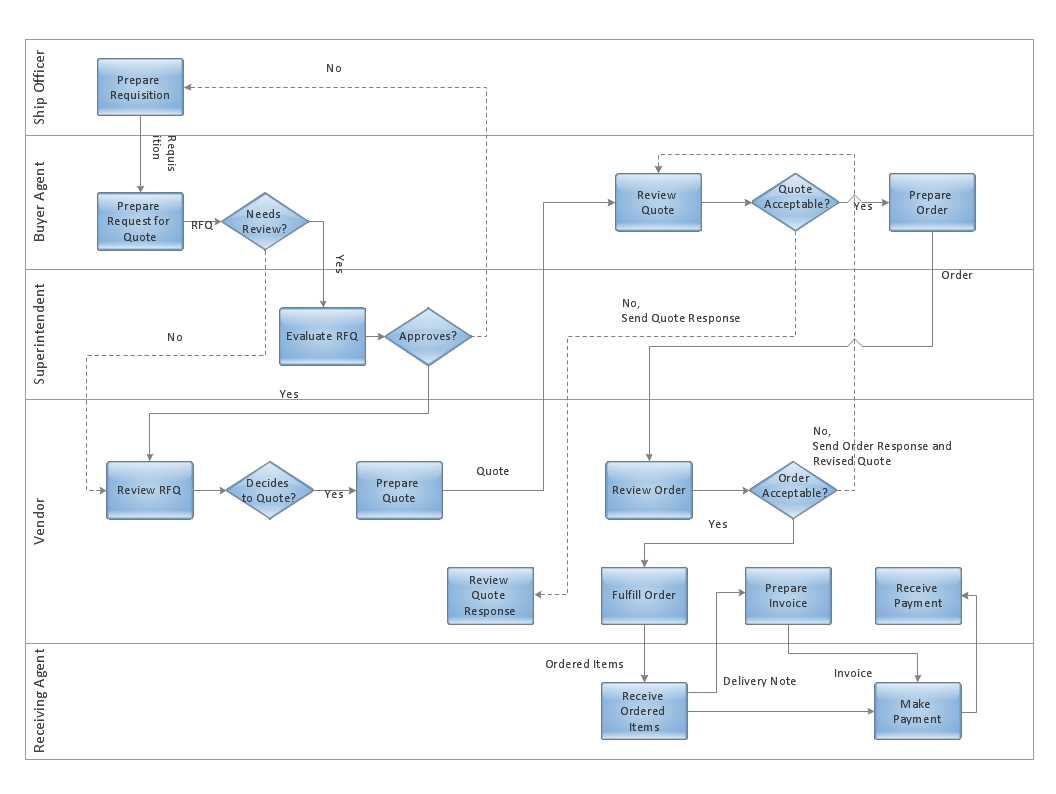
Once you have defined the goals and objectives of your design project in step 2, it is important to gather all the relevant information and data that will be needed to inform and guide your design process. This step involves conducting research, collecting data, and gathering any existing materials or resources that are relevant to the project.
In order to gather this information, you may need to conduct interviews or surveys with key stakeholders, such as clients, users, or subject matter experts. By gathering their insights and input, you can gain a better understanding of their needs, preferences, and expectations. Additionally, it is important to review any existing documentation, such as business plans, market research, or competitor analysis, to gather relevant insights and data.
Once you have collected all the necessary information and data, it is important to organize and analyze it in order to identify any patterns or trends that may be relevant to the design process. This can be done through techniques such as data visualization, content analysis, or thematic analysis. By analyzing the gathered information and data, you can identify any gaps or areas for further research that may be needed to inform your design decisions.
Overall, gathering information and data is a critical step in the design process as it provides the foundation for making informed design decisions. By gathering insights from key stakeholders and analyzing relevant data, you can ensure that your design solution is well-informed and meets the needs of your target audience.
Step 4: Determining the Scope of the Diagram
Once you have identified the objectives of your design process flow diagram, it is essential to determine its scope. This involves specifying the boundaries within which the diagram will capture the design process. Defining the scope helps to avoid including unnecessary or irrelevant information in the diagram.
To determine the scope of the diagram, start by identifying the key stakeholders and their roles in the design process. Consider what activities, decisions, and interactions are essential to include in the diagram to convey the flow of the design process accurately. Determine which phases, steps, or milestones need to be represented and where the diagram should start and end.
It is also crucial to consider the level of detail needed in the diagram. Depending on the target audience and purpose of the diagram, determine whether the diagram should provide a high-level overview or include more granular details. This decision will influence the complexity and size of the diagram.
By determining the scope of the diagram, you can ensure that it effectively communicates the design process while being focused and concise. It allows you to provide the right level of detail to meet the needs of your audience and make the diagram efficient in conveying the essential aspects of the design process.